Deploying ARO Clusters with Pulumi and Infrastructure as code
Published on January 12, 2024 by Ram GopinathanIntroduction
In this post I'm going to walk through deploying Azure RedHat OpenShift clusters with Pulumi and Infrastructure as code. I'm going to assume that you are familiar with Pulumi. If you are new to pulumi I recommend you check out this getting started guide
Pulumi templates are the fastest way to deploy infrastructure to your cloud environments in a consistent and repeatable fashion. Check out this template repo to see a list of available templates. Since there is nothing available for Azure RedHat Openshift I decided to create one. I still haven't contributed this to the template repo yet but for now you can find this in my github here
Before you can get started with this you will need to login to azure portal and request quota increase for compute in EastUS region where we will be deploying the Azure RedHat OpenShift cluster
- Standard DSv3 Family vCPUs = 150
- Total Regional vCPUs = 200
Increasing limits by VM series for Azure Red Hat OpenShift installation is necessary to ensure that your Azure Red Hat OpenShift cluster has the resources it needs to operate efficiently and reliably.
Login to Azure from CLI
Create a directory and cd into it as shown below
mkdir my-aro && cd my-aroCreate a new pulumi project by running command below
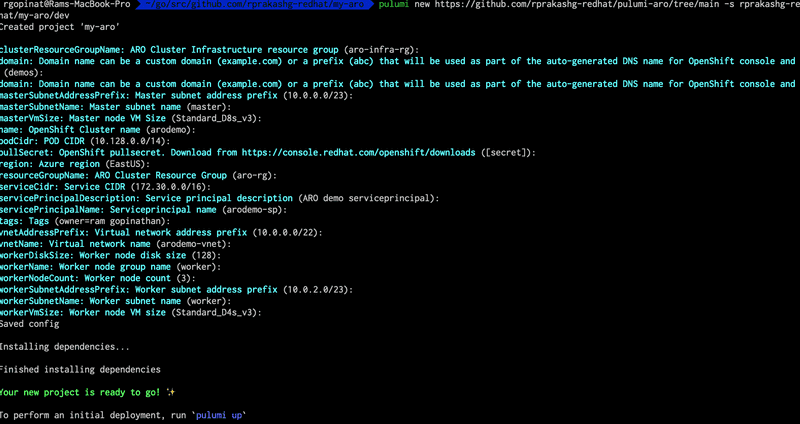
pulumi new https://github.com/rprakashg-redhat/pulumi-aro/tree/main -s rprakashg-redhat/my-aro/devAbove command will prompt to enter configuration values, you can keep the default except the pullSecret which you will need to obtain from console.redhat.com/openshift/downloads See screen capture below
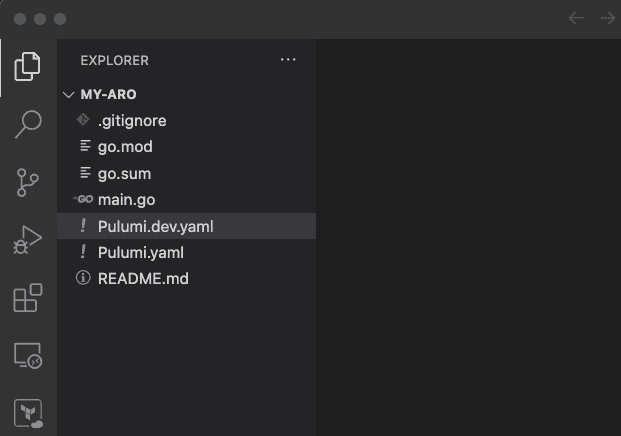
You can open the current folder in visual studio code to see that the project was bootstrapped using the template. You can also see the stack file (dev) that is generated. See screen capture below
Run command below to set the Location on azure-native pulumi provider
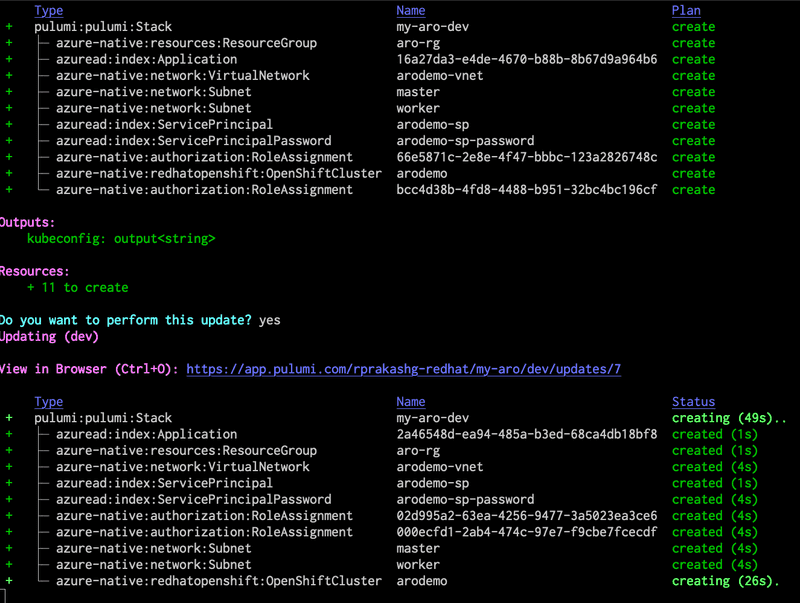
pulumi config set azure-native:location EastUSTo deploy the Azure RedHat OpenShift cluster with pulumi we can simply run pulumi up. Cluster provisioning takes about 50 minutes. You can see output from my environment in the screen capture below
After the cluster provisioning is complete we login to the openshift cluster using the default kubeadmin credentials created. Run the command below to retrieve the default kubeadmin credentials
export CLUSTER=arodemo
export RESOURCEGROUP=aro-rg
az aro list-credentials \
--name $CLUSTER \
--resource-group $RESOURCEGROUPAbove command will return a JSON payload just like what's shown below
{
"kubeadminPassword": "<generated password>",
"kubeadminUsername": "kubeadmin"
}Next we can get the OpenShift console URL by running command below
az aro show \
--name $CLUSTER \
--resource-group $RESOURCEGROUP \
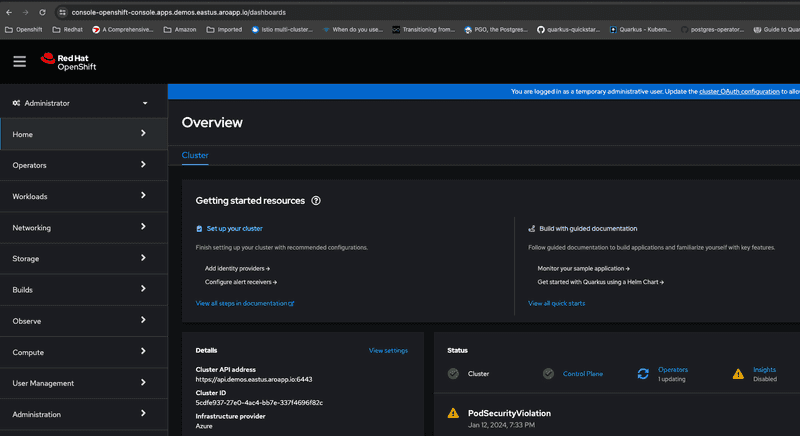
--query "consoleProfile.url"Launch the console in a new web browser and login with default kubeadmin credentials. Screen capture below shows OpenShift console after successfully logging into it
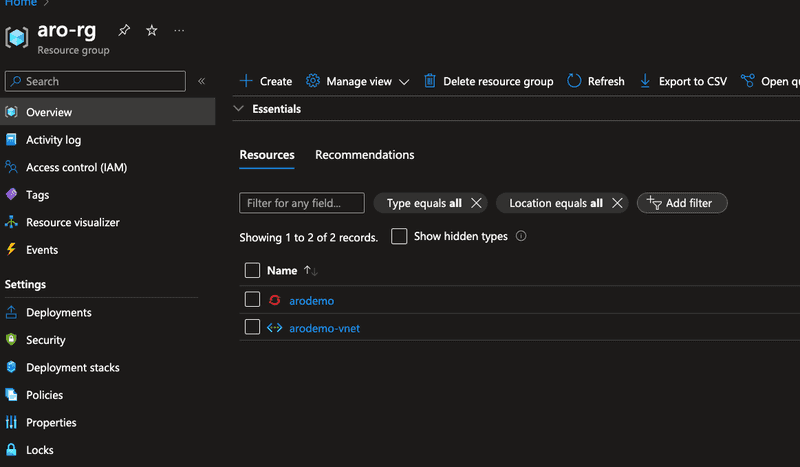
Logging into azure portal we can see aro cluster and vnet in aro-rg resource group as shown in screen capture below
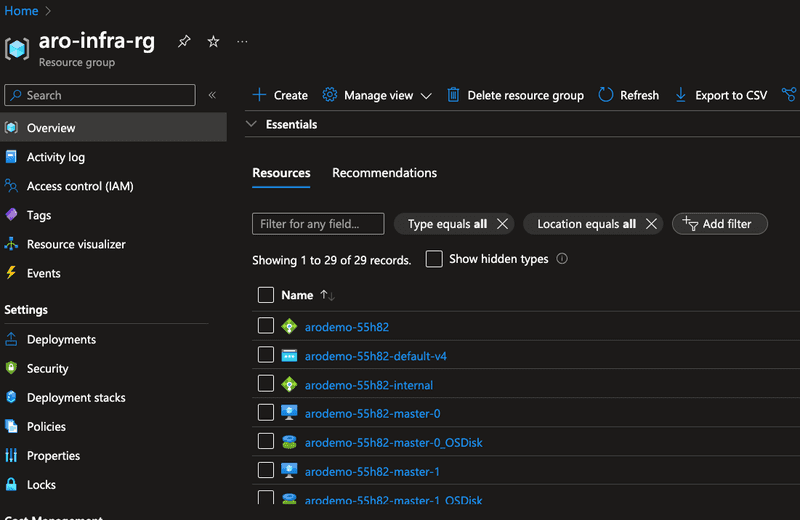
and all the cluster infrastructure resources provisioned in aro-infra-rg as shown in screen capture below
We can run pulumi destroy to delete all the cluster resources. Be sure to do this after you no longer need the resources so that you won't incur any unnecessary charges in Azure
Hope this was helpful and helps you start getting hands on with Azure RedHat OpenShift. If you have any questions about this post or OpenShift please reach out to me via any of the contact methods listed in my blog
Thanks, Ram